Revolutionizing Cancer Diagnostics: Deep Learning and AI in Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) Analysis
Unlocking the Future of Liquid Biopsy: How AI and Deep Learning Are Transforming Cancer Detection with cfDNA Analysis
In recent years, the integration of deep learning and artificial intelligence (AI) with liquid biopsy techniques has unlocked new opportunities for non-invasive cancer diagnostics. Cell-free DNA (cfDNA), which circulates in the bloodstream, carries vital molecular information about tumor presence and progression. By leveraging AI, researchers can now extract meaningful insights from cfDNA, paving the way for earlier cancer detection, monitoring disease progression, and tailoring personalized treatment strategies.
Understanding cfDNA and Its Role in Cancer Detection
What is cfDNA?
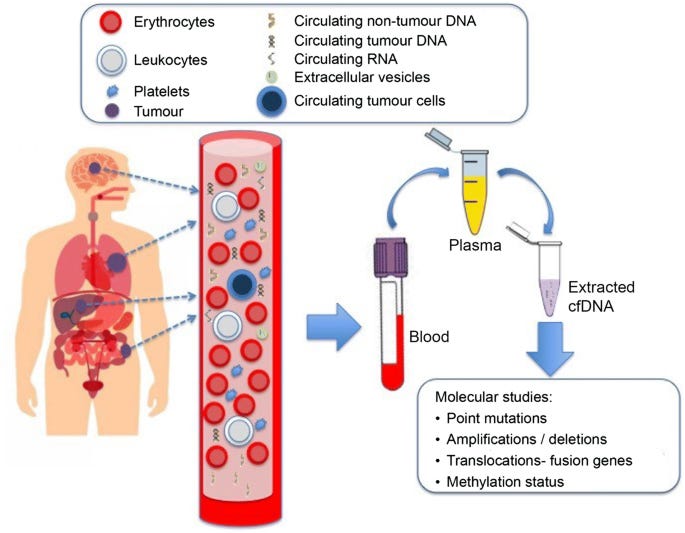
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) consists of short DNA fragments shed into the bloodstream by dying cells. In cancer patients, a subset of cfDNA—called circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)—originates from tumor cells, providing a real-time snapshot of tumor genetics. This makes cfDNA a powerful biomarker for non-invasive diagnostics, commonly referred to as a "liquid biopsy."
Challenges in cfDNA Analysis
Despite its promise, cfDNA analysis faces significant challenges:
Low Tumor-Derived DNA Fraction: Tumor-derived cfDNA is often diluted by normal cfDNA, making it difficult to detect mutations.
High Noise Levels: Technical and biological noise can obscure cancer-related signals.
Complex Data: cfDNA fragmentation patterns, methylation signals, and sequence variations require sophisticated AI-driven analysis for accurate interpretation.
How AI and Deep Learning Enhance cfDNA Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning models overcome these challenges by identifying subtle patterns in large-scale cfDNA datasets. AI-driven approaches integrate multiple data modalities—including DNA sequence, methylation, and fragmentation profiles—to enhance diagnostic precision.
Recent breakthrough studies highlight how AI is revolutionizing cfDNA-based cancer detection and disease monitoring.
Breakthrough Studies in AI-Driven cfDNA Analysis
1. AI-Powered End-Motif Analysis for Cancer Detection
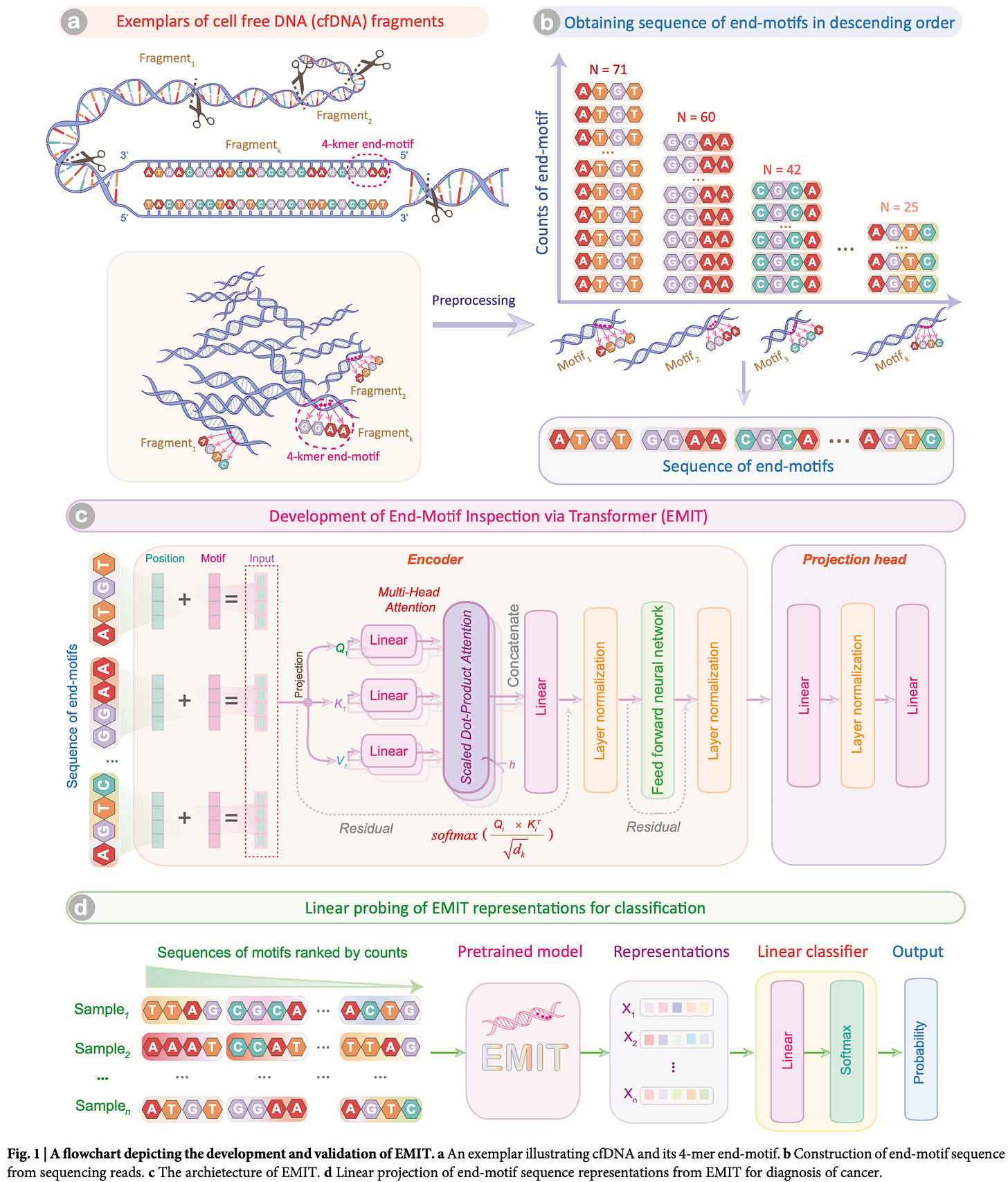
📌 Study: "Development of a Deep Learning Model for Cancer Diagnosis by Inspecting cfDNA End-Motifs"
🔍 Summary:
This study introduces a deep learning model that detects cancer-specific end-motif patterns in cfDNA fragments. Trained on cfDNA sequences from cancer patients and healthy individuals, the model achieved high diagnostic accuracy.
✨ Key Impact:
End-motif patterns contain unique cancer-specific information.
AI-based motif analysis enhances non-invasive early cancer detection.
🛠 Clinical Implications:
This research demonstrates that deep learning can identify subtle sequence-based features in cfDNA that were previously undetectable, improving cancer diagnostics.
2. AI-Integrated Methylation & Fragmentation Analysis for Lung Cancer
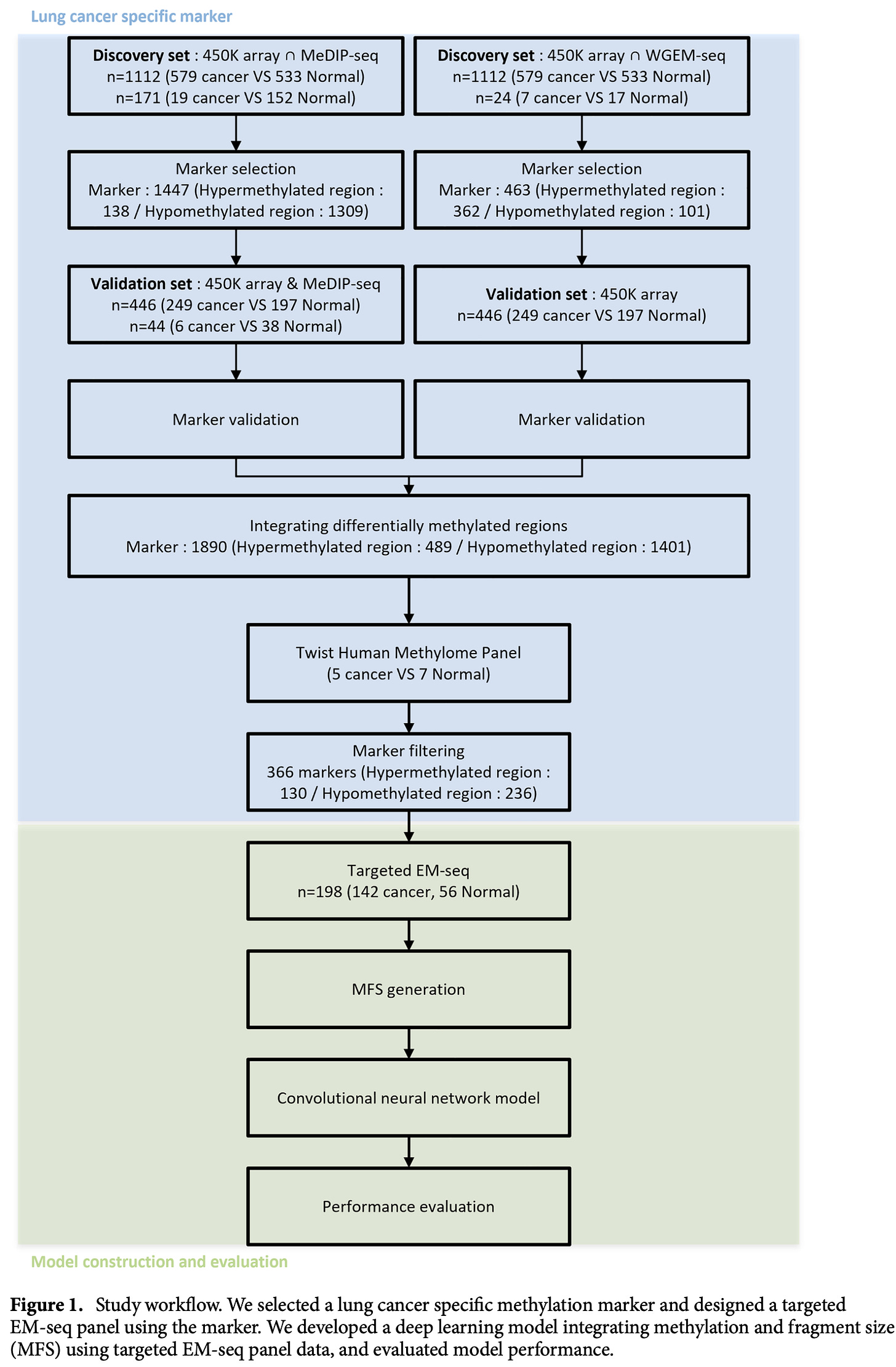
📌 Study: "Deep Learning Model Integrating cfDNA Methylation and Fragment Size Profiles for Lung Cancer Diagnosis"
🔍 Summary:
Researchers developed an AI-driven model that simultaneously analyzes cfDNA methylation and fragmentation profiles to detect lung cancer. The model demonstrated superior diagnostic performance compared to single-feature methods.
✨ Key Impact:
Combining methylation and fragmentation patterns improves cancer detection.
AI enhances multi-omic integration, making liquid biopsy more powerful.
🛠 Clinical Implications:
This study highlights how deep learning can combine multiple genomic signals, improving the sensitivity and specificity of cfDNA-based cancer diagnostics.
3. Tissue Deconvolution Using Deep Learning
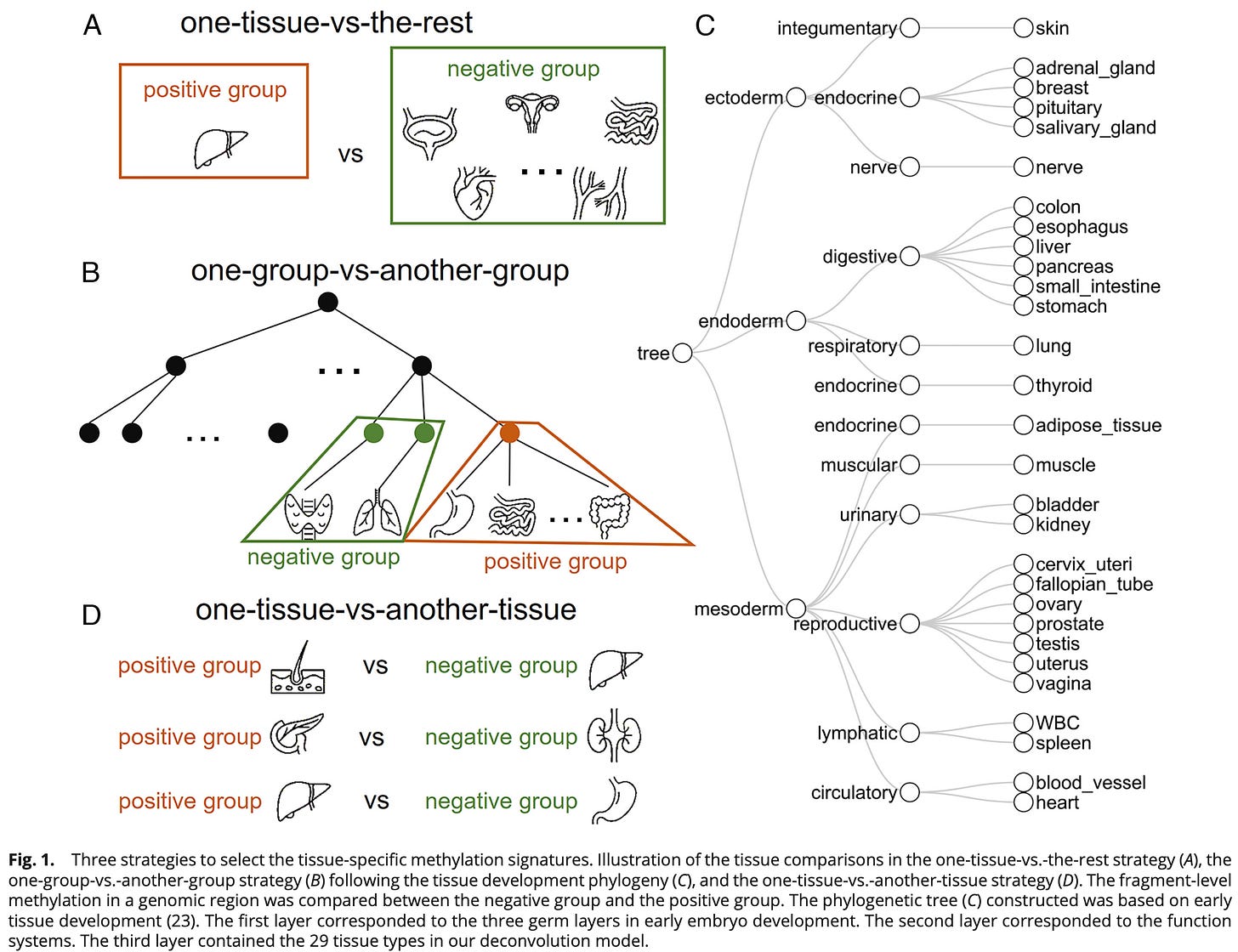
📌 Study: "Comprehensive Tissue Deconvolution of cfDNA by Deep Learning"
🔍 Summary:
This study presents a deep learning framework that determines the tissue-of-origin for cfDNA fragments. By training on multi-tissue cfDNA datasets, the model accurately maps cfDNA fragments to their originating organs.
✨ Key Impact:
Improves specificity in cfDNA-based cancer diagnostics.
Enhances understanding of ctDNA dynamics in blood circulation.
🛠 Clinical Implications:
Pinpointing the tissue of origin helps differentiate between localized and metastatic disease, refining cancer screening strategies.
4. AI for Non-Invasive Pancreatic Cancer Detection
📌 Study: "Precision Oncology: AI, Circulating cfDNA, and Pancreatic Cancer Detection"
🔍 Summary:
This study applies deep learning to genome-wide cfDNA methylation profiling for pancreatic cancer detection. The model achieved 100% sensitivity and specificity in detecting cancer vs. healthy controls.
✨ Key Impact:
AI can decode subtle cancer-linked epigenetic alterations in cfDNA.
Non-invasive pancreatic cancer detection could drastically improve survival rates.
🛠 Clinical Implications:
Given pancreatic cancer's high mortality rate, this research suggests AI-driven cfDNA analysis could be a game-changer for early detection.
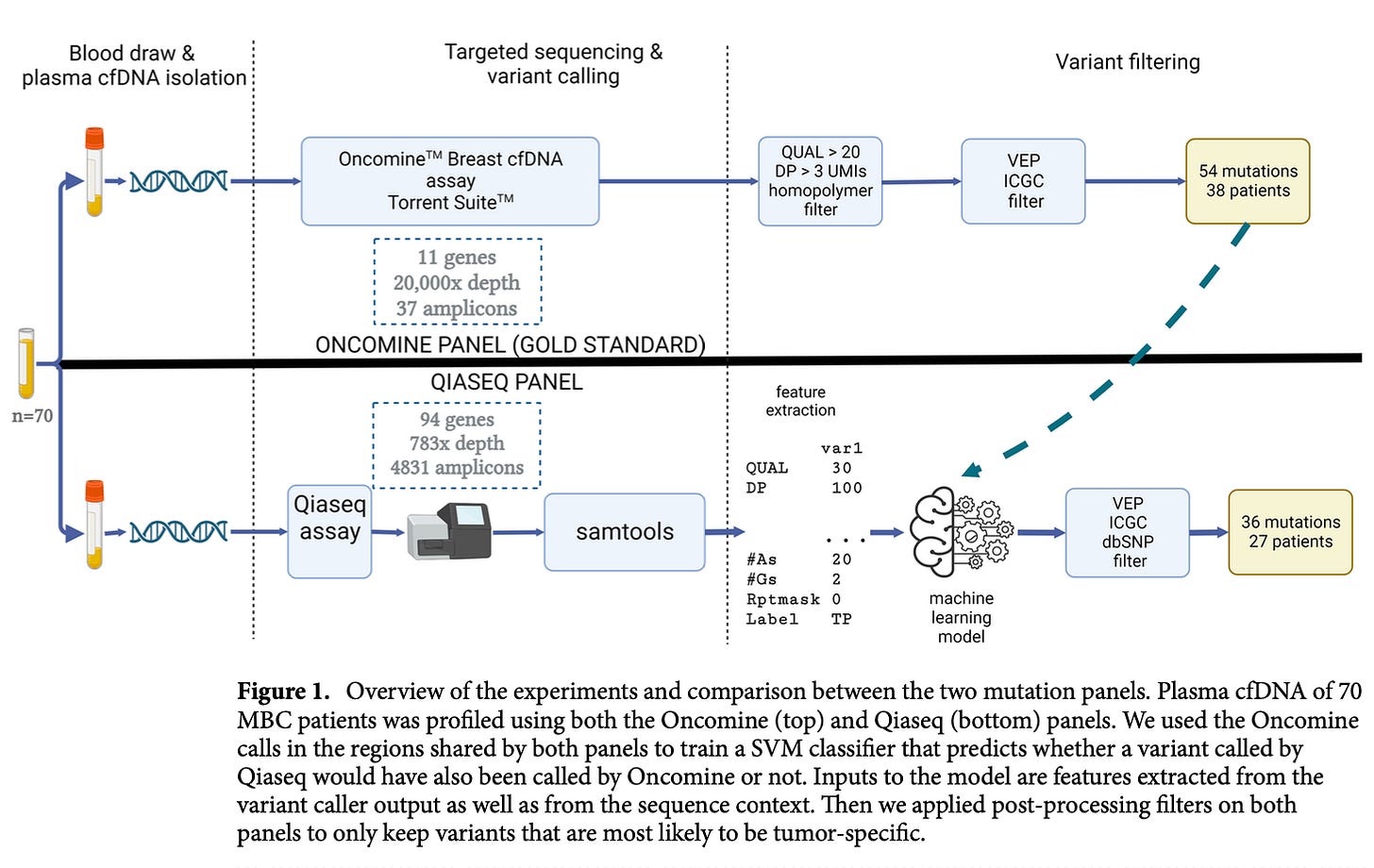
5. AI-Based Somatic Variant Calling in cfDNA
📌 Study: "Machine Learning-Based Somatic Variant Calling in cfDNA of Metastatic Cancer Patients"
🔍 Summary:
This research focuses on improving somatic variant detection in cfDNA using machine learning. The AI model filters false-positive variant calls, ensuring that only tumor-derived mutations are considered.
✨ Key Impact:
Enhances mutation calling accuracy in cfDNA, crucial for monitoring metastatic cancers.
AI reduces false positives, increasing diagnostic confidence.
🛠 Clinical Implications:
This model makes cfDNA-based tumor monitoring more reliable, aiding precision oncology approaches.
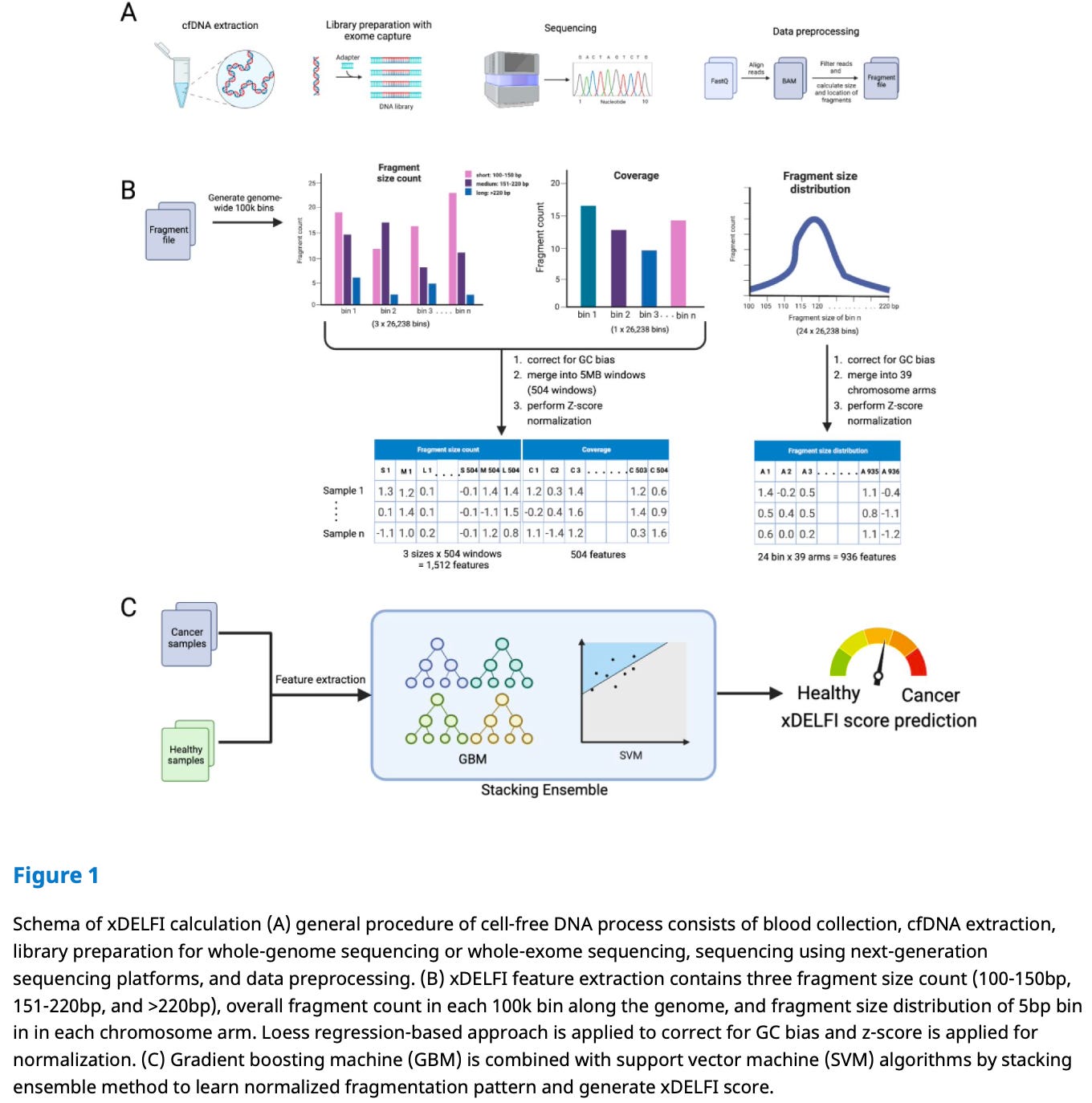
6. Ultra-Low Coverage AI Model for Cancer Detection
📌 Study: "Ultra-Low Coverage Fragmentomic Model of cfDNA for Cancer Detection"
🔍 Summary:
This study presents an AI model that leverages low-depth whole-exome sequencing (WES) of cfDNA for cost-effective cancer screening. The model achieves high diagnostic accuracy at a fraction of sequencing costs.
✨ Key Impact:
Reduces sequencing costs while retaining predictive power.
AI can extract cancer-specific fragmentation patterns even at low coverage sequencing.
🛠 Clinical Implications:
Low-cost cfDNA sequencing methods could make liquid biopsies more accessible worldwide.
Future Directions: AI and cfDNA for Precision Medicine
Key Innovations on the Horizon
Multi-Omic AI Models: Combining cfDNA with proteomics and transcriptomics.
Real-Time Cancer Monitoring: AI-powered cfDNA tracking for therapy response assessment.
Multi-Cancer Early Detection (MCED): AI models screen for multiple cancers simultaneously.
Cost Reduction: Advances in low-cost sequencing + AI will democratize liquid biopsy technology.
Conclusion
The integration of deep learning and AI with cfDNA analysis is revolutionizing cancer diagnostics. AI models can transform cfDNA signals into actionable clinical insights—bringing us closer to non-invasive, early cancer detection and precision treatment strategies.
References
Development of a Deep Learning Model for Cancer Diagnosis by Inspecting cfDNA End-Motifs DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.15.573081
Deep Learning Model Integrating cfDNA Methylation and Fragment Size for Lung Cancer Diagnosis DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-26734-7
Comprehensive Tissue Deconvolution of cfDNA by Deep Learning DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06214-5
Precision Oncology: AI and cfDNA for Pancreatic Cancer Detection DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.014
Machine Learning-Based Somatic Variant Calling in Metastatic Cancer cfDNA DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz498
DISMIR: Deep Learning-Based Noninvasive Cancer Detection DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01283-4
🚀 What are your thoughts on AI-driven liquid biopsy? Let us know in the comments!